Preparation Technology of Spherical Cast Tungsten Carbide Powder
The preparation technology for spherical cast tungsten carbide powder mainly include induction remelting spheroidization method, plasma remelting spheroidization method and plasma rotating electrode atomization method.
The induction remelting spheroidization method uses an induction heating reactor. The material is gradually heated to the spheroidization temperature in the reactor and slowly moves forward relying on the vibration of the furnace tube. Once the dispersion of the material is not controlled well, the molten droplets will Collision and adhesion will cause the particle size to grow, making it difficult to control the particle size; and the powder must not come into contact with the reactor during operation, otherwise it will affect the entire spheroidization process and cause material waste.
The plasma remelting spheroidization method uses cast tungsten carbide powder as raw material, and uses a radio frequency plasma flame to heat the argon gas flow to a high temperature of 3000 to 10000°C, so that the cast tungsten carbide particles melt into a liquid state and are directly and rapidly condensed into spherical particles; this method uses Controlling the particle size state of the raw material affects the particle size and composition of the spherical tungsten carbide powder, and it is easy to obtain finer-grained spherical tungsten carbide powder.
The plasma rotating electrode atomization method uses tungsten carbide rods as electrodes, fixes them in the rod bin, and then performs plasma atomization under inert gas protection. The plasma arc melts the end face of the high-speed rotating bar. Under the action of centrifugal force, the molten droplets break away from the edge of the molten pool and fly and solidify in the form of spherical particles. This technology avoids the problem of difficult material dispersion in remelting spheroidization under ultra-high temperature conditions, and the obtained spherical tungsten carbide powder has a narrow particle size distribution range and is easy to control.
The main components of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder are W element and C element, and they all contain trace amounts of Fe, V, Cr, and Nb elements. The ideal spherical cast tungsten carbide should be a eutectic of WC and W2C, with a eutectic temperature of 2525°C and a carbon content of 3.840% (mass fraction) at the eutectic point. The total carbon content of the spherical cast tungsten carbide prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the smallest deviation from the theoretical value of the eutectic carbon content, and the free carbon content is the lowest; the total carbon content of the powder obtained by the induction remelting spheroidization method has the largest difference with the theoretical value. The value is 0.170% (mass fraction). This is because the induction remelting spheroidization method uses graphite tube heating, which can easily lead to an increase in carbon content. In addition, the powder produced by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has a relatively lowest impurity content. However, the impurity content of the plasma rotating electrode atomization method is relatively high, which may be related to the quality of the cast tungsten carbide raw material rod. Compared with other methods, the plasma rotating electrode atomization method can more accurately control the carbon content of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder, prevent hypereutectic and hypoeutectic reactions caused by carburization and decarburization, and obtain nearly complete eutectic Structure, which is crucial to improving the structure and properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide.
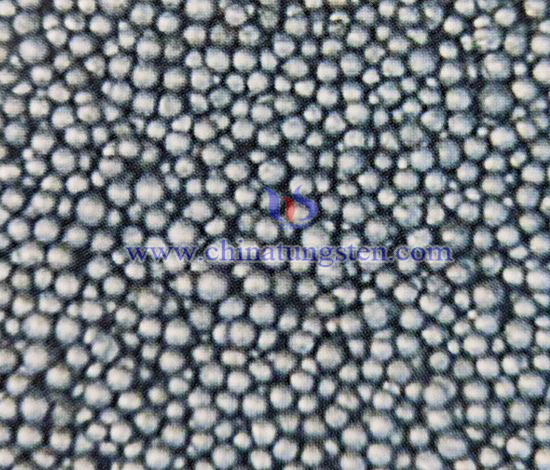

The process technology for preparing spherical cast tungsten carbide powder is mainly to melt the mixture of W, WC, C or conventional cast tungsten carbide particles into a liquid state, and form droplets under the action of external power, and rely on its surface tension to produce cast tungsten carbide. Spherical particles. The preparation technologies and processes of spherical cast tungsten carbide at home and abroad are roughly divided into two categories:
1) Using tungsten powder or tungsten carbide powder as raw material, it is melted into a liquid state through various smelting processes and then made into a spherical shape using various spheroidization techniques (such as atomization), including rotary atomization technology and ultra-high temperature Melting atomization technology.
2) Modify conventional cast tungsten carbide, that is, use conventional cast tungsten carbide as raw material and use a special process (such as plasma melting) to melt the cast tungsten carbide particles into a liquid state and then quickly condense to form spherical particles.
1. Preparation technology using tungsten powder, tungsten carbide powder and carbon (W, WC, C) as raw materials
Rotary atomization technology using water-cooled crucible as smelting equipment. Use tungsten powder as raw material, mix it with carbon black in a disc mill, and then continuously supply the mixture into a water-cooled copper crucible, and use arc to melt it to prepare molten cast tungsten carbide, or use W + WC + C mixture as raw material The self-fluxing electrode arc melting technology, and the self-fusing electrode arc melting technology path using W +WC +C rods as raw materials are also available.
2. Use ultra-high temperature smelting gas atomization technology
The ultra-high temperature smelting gas atomization method is a spherical casting tungsten carbide preparation technology recently successfully developed by a domestic company. It uses tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder as raw materials, mixes the ingredients according to a certain carbon amount requirement, and then pellets it at a certain speed. After being added to the high-temperature smelting gas atomization furnace, the molten liquid enters the high-temperature atomization zone after being melted at a high temperature of nearly 3000°C. Under the high-pressure and powerful impact of the gas, tiny droplets are formed and enter the cooling zone. They are quickly cooled into a spherical shape by relying on their surface tension. Cast tungsten carbide powder.
3. Melting and crushing spheroidization technology
The smelting and crushing spheroidization technology first uses traditional processes to prepare cast tungsten carbide particles, and then heats them by plasma or other heating methods. The cast tungsten carbide particles are remelted and rapidly condensed to turn the irregular powder into regular spheres. Plasma spheroidization technology is a method of preparing spherical particles using plasma as a heating method. Induction heating or resistance heating spheroidization technology uses conventional cast tungsten carbide as raw material, achieves high-temperature melting and rapid condensation spheroidization on ultra-high temperature spheroidization equipment, and controls the temperature under inert gas protection. , raw material particle size, particle size composition, feeding amount, feeding method and screening to prepare multi-grain spherical cast tungsten carbide powder.
The internal structure of the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the three methods is mainly the typical fine needle-like WC and W2C eutectic structure. Compared with plasma remelting spheroidization and induction remelting spheroidization, the eutectic structure of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder produced by plasma rotating electrode atomization method is finer. This is because, compared with the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method, the plasma rotating electrode atomization method completely melts the cast tungsten carbide raw material rod and throws it out to solidify under the action of centrifugal force, and the cast tungsten carbide molten liquid During crystallization, the degree of supercooling is greater, nucleation is faster, and the number of crystal nuclei is larger, so the eutectic structure is more fine. The microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the three methods is all above 2800 HV0.1. Among them, the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the highest microhardness, which can reach 3045 HV0.1. This is mainly due to the finer internal eutectic structure of spherical cast tungsten carbide produced by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method. The characteristics of the three processes for preparing spherical cast tungsten carbide are as follows:
(1) The total carbon content of spherical cast tungsten carbide prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the smallest deviation from the theoretical value of the eutectic carbon content, the free carbon content is the lowest, and the impurity content is relatively low.
(2) The interior of the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method is dense, with almost no defects, and the eutectic structure is finer. The interior of the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method is There are some obvious pores, that is, some hollow powder appears.
(3) The spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the three methods mainly contains WC and W2C phases.
(4) The microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the three methods is all above 2800 HV0.1. Among them, the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the highest microhardness, which can reach 3045 HV0.1. The powder produced by the induction remelting spheroidization method has the best fluidity and the highest bulk density.
If you have any interest in spherical cast tungsten carbide powder, please feel free to contact us by email: sales@chinatungsten.com or by telephone: +86 592 5129696.
More info>>
