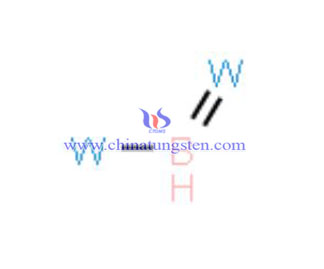
Tungsten Boride

Introduction
Name: Boranylidyne Tungsten
Name: Tungsten Monoboride; Tungsten Boride
CAS: 12007-09-9
Formula: BH2W
Formula: 196.66700
Exact Mass:196.97600
Tungsten boride usually refers to binary compound which is combined of metal and boron, normal valence boride which is rare, is also known as the normal valence of boron salts Mg 3B 2, CrB etc., the majority are interstitial compounds which do not meet the inter-valence charge. These compounds may be represented as MBx (x is a positive integer). When x=2, that MB 2 (M = Al, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, U, Mn, Co, Ni); when x=6, MB 6 (M = Ca, Sr, Ba, V, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Cd, Er, Y, Si, Th); the amount of boride when X= 1, 4 12 is relatively small.
Nature
Silver white octahedral crystal, the density is 10.77g/cm3, the melting point is 2900℃. Tungsten boride is insoluble in water, it was dissolved in aqua regia and some concentrated acid. It can be decomposed by chlorine gas at 100℃. The tungsten boride can be generated by direct heating metal tungsten and boron in a electric heating furnace
Application
Tungsten boride, the melting point is 3040℃, can be used as refractory; In addition, many of them used as boride ceramic materials, seen as the generalized silicate material. The commonly used are zirconium diboride (ZrB2), lanthanum hexaboride (LaB6), titanium diboride (TiB2), boron tantalum (TaB2), chromium boride (CrB), tungsten boride (W2 B5), of which chromium boride, tungsten boride are commonly used as solid filler in wear-resistant coating.